
- Home
- About
- Our Team
- Services
- Postoperative Care
- Smile Gallery
- Medical Tourism
- Blog
- Offers
- Contact Us
- Home
- About
- Our Team
- Services
- Postoperative Care
- Smile Gallery
- Medical Tourism
- Blog
- Offers
- Contact Us
Gingival recession, often known as gum recession, is a disorder that affects many people, frequently without knowing it until the symptoms become apparent. Addressing early gum recession is critical to preserving excellent oral health and avoiding more significant dental disorders in the future. In this blog, we’ll look at numerous treatment options to help you rebuild your gums and safeguard your teeth, resulting in a healthier, more confident smile.
Gingival recession, also known as gum recession, is a dental disease in which the gum tissue around the teeth gradually decreases, exposing more of the tooth or its root. It can cause dental discomfort, an increased risk of decay, and cosmetic issues. Aggressive brushing, poor dental hygiene, periodontal disease, or genetic susceptibility are all common causes of gingival recession, which can worsen over time if not treated.
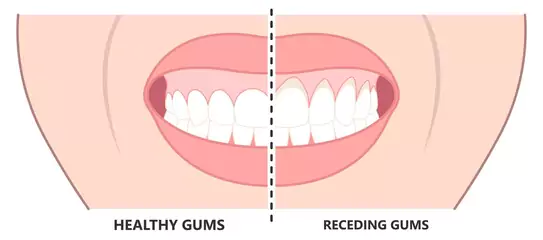
Understanding the reasons for gingival recession is the first step towards avoiding and treating the problem. Various causes might cause gum recession:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can cause plaque to build up and harden into tartar. It might irritate your gums, resulting in a gingival recession.
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing your teeth too aggressively or using a toothbrush with firm bristles might cause your gum tissue to recede.
Periodontal Diseases: This is an advanced form of gum disease that destroys the soft tissue and bone that support your teeth, resulting in significant gingival recession.
Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to gum recession. Therefore, it is critical to check gum health regularly to see if you have a family history of dental problems.
Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products can cause your gums to recede by decreasing blood supply to the gum tissue, limiting its capacity to repair.
Hormonal Changes: Women may experience gum recession during pregnancy, menopause, or menstruation due to hormonal changes that make the gums more sensitive.
Early detection of gingival recession can help to prevent it from progressing to more severe problems. Here are some indications to look for:
Teeth Sensitivity: If you have heightened sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet meals, this might be an indication of early gum recession.
Longer teeth: As the gums recede, your teeth may look longer than usual. It is an obvious indication that the gum tissue is pushing back.
Exposed Roots: If your teeth’s roots are exposed, this is a definite sign of gingival recession.
Bleeding gums: If your gums bleed when brushing or flossing, this might be the result of early gum recession or gum disease.
There are various successful gingival recession treatments available, including non-surgical and surgical methods. Your dentist will offer the most appropriate therapy based on the severity of your issue.
Your dentist will clean the root surfaces beneath the gum line to eliminate plaque and tartar. The roots are then flattened (planed) to allow the gums to reconnect to the tooth. This therapy is particularly successful in reversing early gum recession caused by plaque accumulation.
Gum grafting is a surgical treatment that treats severe gingival recession. It entails removing tissue from another section of your mouth (typically the palate) or applying donor tissue to conceal the exposed root. This helps to repair the gum line and protects the roots of your teeth.
The pinhole surgical method is a minimally invasive surgery that includes making a tiny hole in the gum tissue. Through this hole, the dentist uses special devices to loosen the gum tissue and glide it over the exposed roots. This procedure involves no sutures and has a faster recovery period than standard gum grafting.
Soft tissue grafts, like gum grafting, entail transferring tissue from the roof of your mouth or a tissue bank and connecting it to the area where the gums have receded. This not only covers the exposed roots but also strengthens the gum tissue, giving it further protection against future recession.
Laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment for mild to severe gum recession. A dental laser is used to eliminate unhealthy gum tissue while stimulating the creation of new, healthy tissue. This can assist to reverse gingival recession and decrease the depth of periodontal pockets.
Desensitizing drugs can be used to treat tooth sensitivity caused by early gum recession. These compounds aid in alleviating irritation and pain while preserving the exposed roots from additional harm.
It is always better to prevent than to cure. Here are some tips for preventing gingival gum recession:
Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss regularly to eliminate plaque and food particles that can cause gum disease.
Use the proper brushing technique: Avoid vigorous brushing. Instead, apply moderate circular strokes with the brush angled at 45 degrees to your gum line.
Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist on a regular basis for expert cleanings and examinations. Early identification of gum recession allows for more successful therapy.
Quit smoking: Quitting smoking can greatly improve gum health and lower the risk of severe gingival recession.
Wear a mouthguard: If you grind your teeth at night (bruxism), a custom-fitted mouthguard can help protect your teeth and gums from harm.
Gingival recession is a common dental problem that can have significant consequences if not resolved. Understanding the reasons for gum recession, identifying the early warning symptoms, and seeking immediate treatment are essential steps toward safeguarding your dental health. Whether you have early or severe gingival recession, there are effective treatments available to help reverse the damage and restore your smile. Maintaining proper dental hygiene and taking preventive steps will help you keep your gums healthy while avoiding the discomfort and visual difficulties associated with gum recession.
Gingival recession can be fixed with techniques like scaling and root planning, gum grafting, and the pinhole surgical approach.
To prevent gum recession, maintain proper oral hygiene, use a soft-bristled toothbrush, and schedule frequent dental visits.
Saltwater rinses can help decrease irritation, but they will not restore receding gums. They assist in keeping your mouth clean and minimize germs.
Toothpaste for sensitive teeth, such as Sensodyne or Parodontax, is frequently advised for receding gums.
To minimize further discomfort and damage to receding gums, use a soft-bristled, manual or electric toothbrush.